Sodium Tripolyphosphate (STPP) and Sodium Hexametaphosphate (SHMP). Both help control hardness-related issues—but they are not interchangeable.
Quick access
Product specs:
Industrial Grade STPP | SHMP 68% |
Solution hub:
Water Treatment Chemicals
Jump to:
TOC | Selection Matrix | P2O5 Verification | ROI Worksheet | Downloads | FAQ
Reading shortcuts by role
- Water Treatment Engineer: Sections 2–7 (mechanisms → STPP/SHMP → matrix → dosage → verification).
- Procurement / Buyer: Sections 8–12 (spec traps, COA checks, documentation, supply, downloads).
- Plant Manager: Sections 1 + 9 (cost framing + ROI worksheet + action checklist).
Table of Contents
- Why Scale Is More Than “Just Deposits”
- How Phosphates Work: Sequestration + Threshold Effect
- Role of STPP in Water Conditioning
- SHMP 68%: A Strong Option for Demanding Scale Control
- STPP vs SHMP: Quick Comparison
- Scenario-Based Selection Matrix (Cooling Tower / Boiler / Ceramics / Textile)
- Starting Dosage & Monitoring Checklist
- The P2O5 Trap: How to Verify “Real 68%”
- ROI Worksheet (Energy + Downtime + Chemical Spend)
- Customer Case
- Why Buyers Trust Goway Chemical
- Tools & Downloads
- Ready to Optimize?
- FAQ
1) The Hook: Why Scale Is More Than “Just Deposits”
Industrial scale is not only a visual nuisance. Even thin layers of scale can reduce heat transfer, forcing boilers and heat exchangers to consume more energy to reach the same output.
In cooling towers, scale narrows flow paths, raises pumping costs, and increases the risk of unplanned downtime. Over time, scale can also contribute to under-deposit corrosion, putting equipment lifespan and safety at risk.
The most common culprits are hardness ions such as calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+). When these ions combine with carbonates or sulfates, they form insoluble deposits that adhere to metal surfaces. The goal of modern water conditioning is to keep these ions controlled—before they form hard scale.
Fast recommendation (engineer-to-engineer)
Share system type (cooling tower/boiler/ceramics/textile), operating temperature, water hardness, and current cleaning frequency.
We’ll reply with a starting selection + dosage window + monitoring checklist.
2) The Science of Sequestration (Plus Why Programs Work Better Than “One Chemical”)
Both STPP and SHMP work through sequestration: they bind multivalent metal ions (such as Ca2+ and Mg2+) to form stable, soluble complexes.
When hardness ions are “locked” into soluble complexes, they are less likely to react with carbonates or sulfates to form stubborn deposits.
Many industrial systems also benefit from a second effect—often called a threshold effect: the right phosphate program can interfere with scale crystal growth at low dosage, reducing the chance that deposits become hard and adherent. In real plants, best results usually come from a treatment program (scale inhibitor + dispersion strategy + operational control), not a “single-product fix.”
| Mechanism (plain language) | What it does | Where you feel it fastest |
|---|---|---|
| Sequestration (hardness locking) | Reduces Ca/Mg “available” to form deposits | General process water, cooling tower make-up variability |
| Threshold effect (crystal control) | Slows scale growth when dosage and monitoring are stable | Cooling towers (higher cycles), stable loops |
| Dispersion | Keeps particles suspended, reduces surface deposition | Ceramics slurry, turbid loops |
| Operational control | Blowdown / pH / hardness stability drives repeatability | Boilers and cooling towers |
3) Role of STPP in Water Conditioning
Sodium Tripolyphosphate (STPP) is widely used in industrial cleaning and general water conditioning. It performs well in many low-to-medium temperature systems and is frequently selected when a balance of sequestration and operational stability is needed.
- Best for: Low to medium temperature systems, industrial detergents, and cleaning formulations.
- Key advantage: Supports alkalinity buffering and helps stabilize pH in certain processes.
- Typical value: A reliable conditioner where scale risk is moderate and “cleaning synergy” matters.
For detailed specs and supply options, review: Industrial Grade STPP.
4) SHMP 68%: The Powerhouse of Scale Inhibition (Plus ROI Logic)
For higher-efficiency scale control, Sodium Hexametaphosphate (SHMP)—especially the 68% P2O5 grade—is often the preferred choice in demanding industrial systems.
SHMP is widely applied in boiler water treatment, cooling towers, ceramics, and other processes where scale control must be strong and consistent.
- Thermal stability (program-dependent): Often selected for more demanding operating conditions.
- Threshold effect: Can slow scale crystal growth at relatively low dosages when optimized and monitored.
- Ideal use cases: Boilers, cooling towers, higher-hardness loops, ceramics dispersion, and applications requiring consistent scale inhibition.
ROI logic engineers can defend:
In high-temperature or high-hardness systems, SHMP can cost more per ton than STPP, but it may reduce total program cost through lower dosage needs and fewer cleaning shutdowns. Example scenario (illustrative): even if SHMP is ~18% higher in unit price, a tuned program can achieve ~25% lower chemical usage and ~60% fewer cleaning events, leading to a ~32% lower total cost. Actual results vary by water chemistry, cycles, temperature, and operational controls—validate via a short pilot and monitoring logs.
For detailed specs and consistent supply, explore: SHMP 68%.

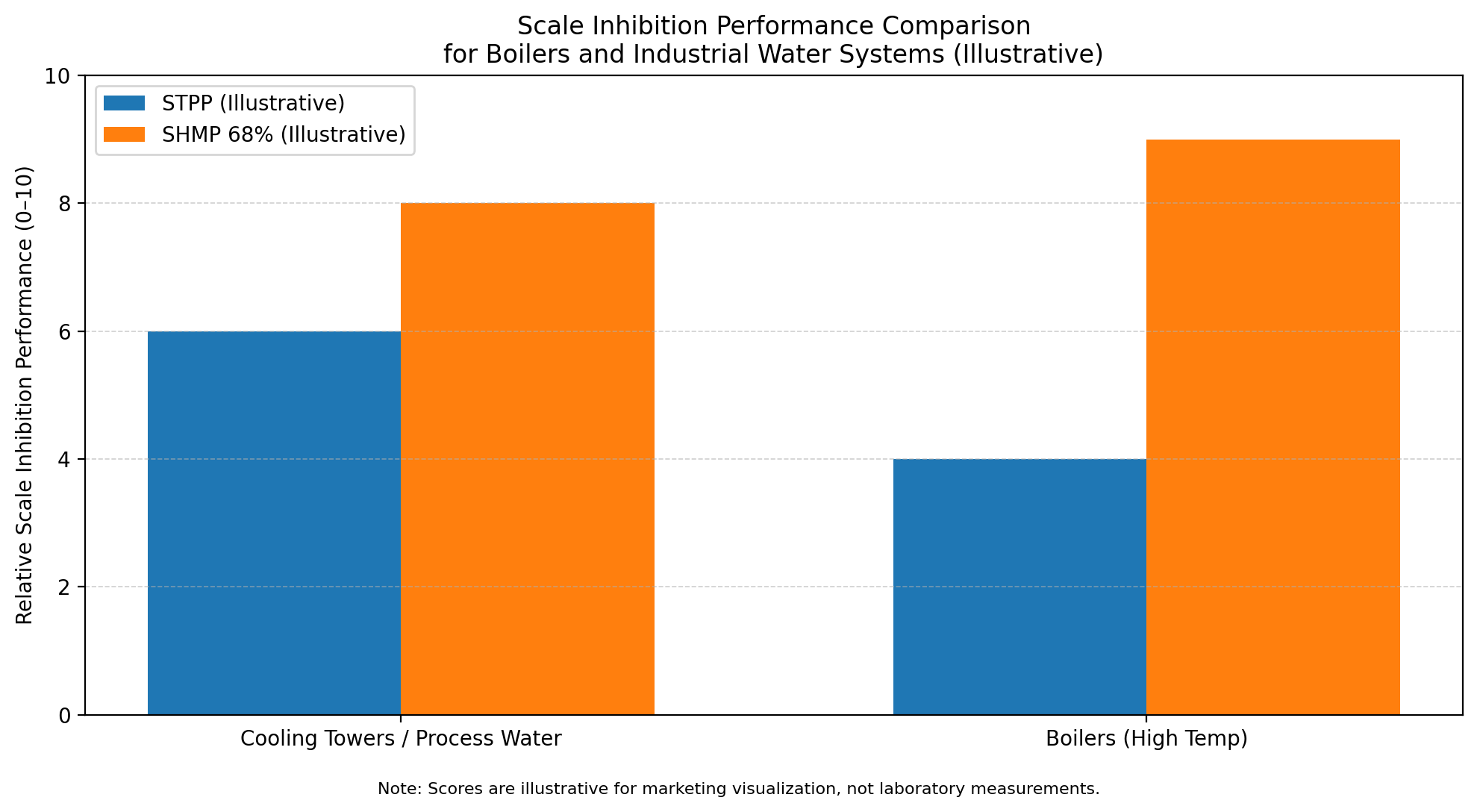
5) STPP vs. SHMP: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | STPP | SHMP (68%) |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Softening & Buffering | Advanced Scale Inhibition |
| P2O5 Content | Approx ~57% (industrial grade) | 68.0% Min (verify via COA) |
| Temperature Tolerance | Moderate | High (commonly selected for demanding loops) |
| Common Application | Detergents, general water conditioning | Boilers, cooling towers, ceramics |
Practical selection tip: Moderate temperatures + need process stability → STPP is often a solid option.
Boilers, high-hardness loops, and scale-critical cooling systems → SHMP 68% is commonly favored for stronger scale inhibition.
Prefer email? Write to: [email protected]
6) Scenario-Based Selection Matrix (Cooling Towers, Boilers, Ceramics, Textile)
The fastest way to choose is to match phosphate selection to temperature, hardness load, and process risk.
Use this as a practical starting matrix, then validate with a short pilot and monitoring checklist.
| Application | Recommended starting approach | Typical starting window | Key control targets | Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-temp boilers (>100°C) | SHMP 68% first (validate in your system) | Start ppm-level; tune by blowdown and deposit indicators | Hardness control, blowdown discipline, deposit trend | Skipping COA verification; no monitoring logs |
| Cooling towers (moderate-to-high cycles) | STPP + SHMP blend (simple, then optimize) | Start ppm-level; tune by cycles and deposit/flow KPIs | Cycles, conductivity, hardness drift, pH stability | Overdosing; ignoring make-up water variability |
| Ceramics slurry / process water | SHMP 68% (dispersion & purity focus) | Often ~0.3%–0.5% (process dependent) | Viscosity, turbidity, insolubles, defect trend | Impurity-driven defects; inconsistent dissolution |
| Textile & dyeing | STPP (hardness control + pH stability) | Process-dependent; stabilize pH window and hardness drift | pH window, bath clarity, shade consistency | Skipping pH checks; hardness spikes causing precipitation |
7) Starting Dosage & Monitoring Checklist
Scale inhibition is rarely a “product problem.” It’s usually a control problem. The best plants standardize: dosing method, test frequency, and acceptance KPIs (deposit trend, flow trend, energy KPIs).
Starting dosage guidelines (trial-first)
Because water chemistry varies by plant, treat these as starting trial ranges only (validate before scaling):
- Cooling towers: ppm-level dosing is typical; tune by cycles/hardness trend and deposit inspections.
- Boilers: ppm-level dosing is typical; tune by blowdown control and deposit indicators.
- Ceramics: commonly ~0.3%–0.5% SHMP where dispersion is critical (process dependent).
- Textile: focus on stable pH window and hardness drift control; dosing depends on bath conditions.
Minimum monitoring checklist
| System | Daily | Weekly | Monthly |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling tower | Conductivity, pH, blowdown status | Hardness (Ca/Mg), turbidity | Deposit trend + energy/flow KPIs |
| Boiler | Blowdown control + feed hardness trend | Deposit indicators, alkalinity trend | Heat transfer KPIs + inspection record |
| Ceramics | Viscosity/turbidity stability | Insolubles/Fe checks as needed | Defect rate + rework frequency |
| Textile | pH window stability | Hardness drift + bath clarity | Shade consistency + precipitation incidents |
8) The P2O5 Trap: How to Verify “Real 68%” SHMP
P2O5 content is a standard metric for phosphate concentration. But not every “68%” grade in the market is truly 68%.
Use these checks before scaling procurement:
3-step verification method
- COA wording check: Must state “Total Phosphate (as P2O5) ≥ 68.0% min” (not “about 68%”).
- Dissolution behavior check: Test dissolution consistency in your real water (time-to-clear + any residue).
- Storage discipline: Keep powder dry and sealed; use fresh liquid solution on a controlled schedule to reduce hydrolysis/instability risk.
Want the printable checklist?
Download the Industrial Water Phosphate Selection Checklist (includes COA wording examples + a simple water test template), or get it instantly on WhatsApp by sending: Water Guide.
9) ROI Worksheet: Prove Savings (Energy + Downtime + Chemical Spend)
If you want management approval, quantify results. This worksheet converts scale prevention into a clear business case.
(For a ready-to-use file, download the ROI template below.)
| ROI input | Your value | How to use it |
|---|---|---|
| System type | _____ | Cooling tower / Boiler / Ceramics / Textile |
| Operating temperature | _____ °C | Selection driver |
| Water hardness | _____ ppm as CaCO3 | Scaling risk indicator |
| Annual energy spend | _____ / year | Track before vs after KPIs |
| Cleaning cost | _____ / year | Chemicals + labor + parts |
| Downtime loss per event | _____ / event | Production loss per stoppage |
ROI outputs to report: fewer cleaning events/year, fewer downtime hours/year, improved energy KPI trend, and payback period (months).
10) Customer Case (Trust Booster)
Customer case: Global Chemical Plant (high-pressure boiler program)
- Pain point: High-pressure boiler (~120°C) scaling issues; shutdown cleaning every 3 months.
- Solution: Switched to Goway SHMP 68% with a controlled dosing window (8 ppm) and monitoring checklist.
- Results: ✅ Cleaning cycle extended to 8 months | ✅ Annual maintenance savings: $180,000 | ✅ Estimated equipment life extension: 2.3 years.
Note: Results depend on system conditions and operational controls. Use a short pilot + monitoring logs to validate in your plant.
11) Why Buyers Trust Goway Chemical
In industrial water treatment, performance consistency matters as much as chemistry selection. A small variation in active content or impurity profile can cause dosing instability and operational risk.
Goway Chemical focuses on what procurement teams and engineers care about most:
- Stable specifications for predictable performance and dosing control
- Quality documentation support (COA/TDS/SDS workflows for industrial sourcing)
- Responsive technical communication to align product choice with system conditions
- Bulk supply reliability for ongoing treatment programs and long-term projects
12) Tools & Downloads (SEO + Lead Capture Boost)
Replace the placeholder links below with your WordPress Media Library URLs:
Industrial Water Phosphate Selection Checklist (with water test template) – PDF
Ready to Reduce Scale Without Over-Spending Chemicals?
Get a system-specific recommendation (STPP vs SHMP vs blend), a starting trial window, and a monitoring checklist.
We can also provide procurement-ready documentation (COA/TDS/SDS) and bulk pricing.
Prefer email? [email protected]
FAQ
Is SHMP effective in high-temperature boilers?
SHMP is widely used for industrial scale control and is commonly selected when stronger hardness control is needed in demanding systems.
Final selection and dosing should be validated in your operating conditions (hardness load, cycles, temperature, and monitoring KPIs).
Can STPP be used as an industrial water softener?
Yes. STPP is commonly used in water conditioning and industrial cleaning. It helps sequester hardness ions and can support operational stability in many low-to-medium temperature applications.
How do I choose between STPP and SHMP for scale prevention?
Start with system temperature, scaling risk, and mineral load. STPP is often chosen for general conditioning and buffering benefits in moderate conditions, while SHMP 68% is typically preferred for stronger scale inhibition in boilers, cooling towers, ceramics, and higher-risk scaling systems.
What documents do industrial buyers typically request?
Most procurement teams request lot-specific COA, TDS, SDS, packaging details, and a brief usage guidance note (trial window + monitoring checklist).
For projects requiring “68% P2O5,” explicit COA language and verification steps are recommended before scaling procurement.
