Products
Industrial chemicals & food-grade phosphates. Specs, packaging and supply terms.
Explore Products
Applications
Industry landing pages built for buyers: pain points → recommended grades → quote.
View Applications
Technical Guides
Encyclopedia & super pages that answer questions and drive inquiries.
Browse ResourcesCore Industrial Phosphates
Focused product lines for engineering-grade applications. Click to get technical data or request samples.

STPP (Industrial Grade)
The #1 choice for ceramic deflocculation and detergent builders.
Get STPP Technical Data Request STPP Sample
SHMP (Industrial Grade)
Superior dispersant for water treatment and industrial cleaning.
Get SHMP Technical Data Request SHMP Sample
TSPP (Industrial Grade)
High-pH buffer and chelator for specialized applications.
Get TSPP Technical Data Request TSPP QuoteBy Applications
Trusted by Global Industries for Over a Decade
Our phosphates deliver proven performance in water treatment, ceramics, and industrial cleaning.
Technical Guides
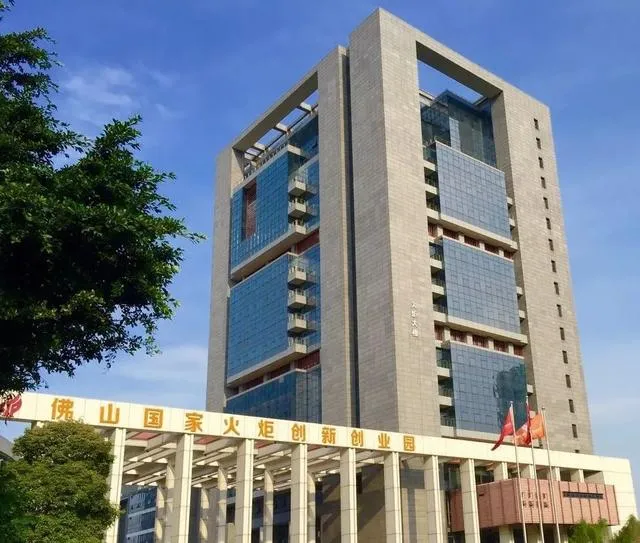

Phosphate Manufacturer
GOWAY INTERNATIONAL MATERIAL CO., LTD has focused on phosphates for over 10 years. Our factory in Sanshui Industrial Zone covers 60,000 square meters with a single-line capacity of 30,000 tons. We supply industrial & food-grade phosphates with stable quality and technical support.
Export-ready documents available: COA / MSDS / packing & loading plan. Factory audit support on request.
Company & Factory Contact SalesHot-Sale Products
6 key SKUs buyers ask for most. Click to download technical data or request a sample/quote.

STPP (Industrial)
Sodium Tripolyphosphate
#CeramicDeflocculant#DetergentBuilder
Get STPP Technical Data Request STPP Quote
STPP (Food Grade)
Sodium Tripolyphosphate
#MeatProcessing#MoistureRetention
Get STPP Food Technical Data Request STPP Sample
SHMP (Industrial)
Sodium Hexametaphosphate
#WaterTreatment#Dispersant
Get SHMP Technical Data Request SHMP Quote
SHMP (Food Grade)
Sodium Hexametaphosphate
#SeafoodProcessing#TextureControl
Get SHMP Food Technical Data Request SHMP Sample
TSPP (Industrial)
Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate
#Buffer#Chelator
Get TSPP Technical Data Request TSPP Quote
TSPP (Food Grade)
Tetrasodium Pyrophosphate
#Baking#pHControl
Get TSPP Food Technical Data Request TSPP SampleHow We Support Your Purchase
- Grade Recommendation: Industrial/Food grade selection based on your application.
- Specs & Documents: Technical data, COA/MSDS, packaging & loading plan.
- Sampling: Fast samples with stable batch control.
- Production & QC: Consistent inspection before shipment.
- Logistics: Flexible shipping terms and reliable delivery.
Why Buyers Choose Goway

>10 Years Manufacturing
Fully automated STPP production line | Process & QC experienced team.

Consistent Quality
Batch-to-batch stability | Example spec: P₂O₅ ≥ 57% (replace with your real spec).

Supply & Delivery
30,000 tons annual capacity | Reliable lead time & logistics support.

Export-Ready Documents
COA / MSDS / packing & loading plan | Factory audit support on request.












































